In Antarctica, a new record minimum sea ice extent of 2 million quadrad kilometers was reached on February 19; meanwhile, the ice area here is increasing again. On the other side of the world, in the Arctic, the annual maximum ice area was recorded on March 6.
Low sea ice extent in the Arctic
This was 14.62 million square kilometers. The value is based on data from the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's (JAXA) GCOM-W1 satellite and is the 5th lowest since 1979, 1.03 million square kilometers below the 1980-2010 average.
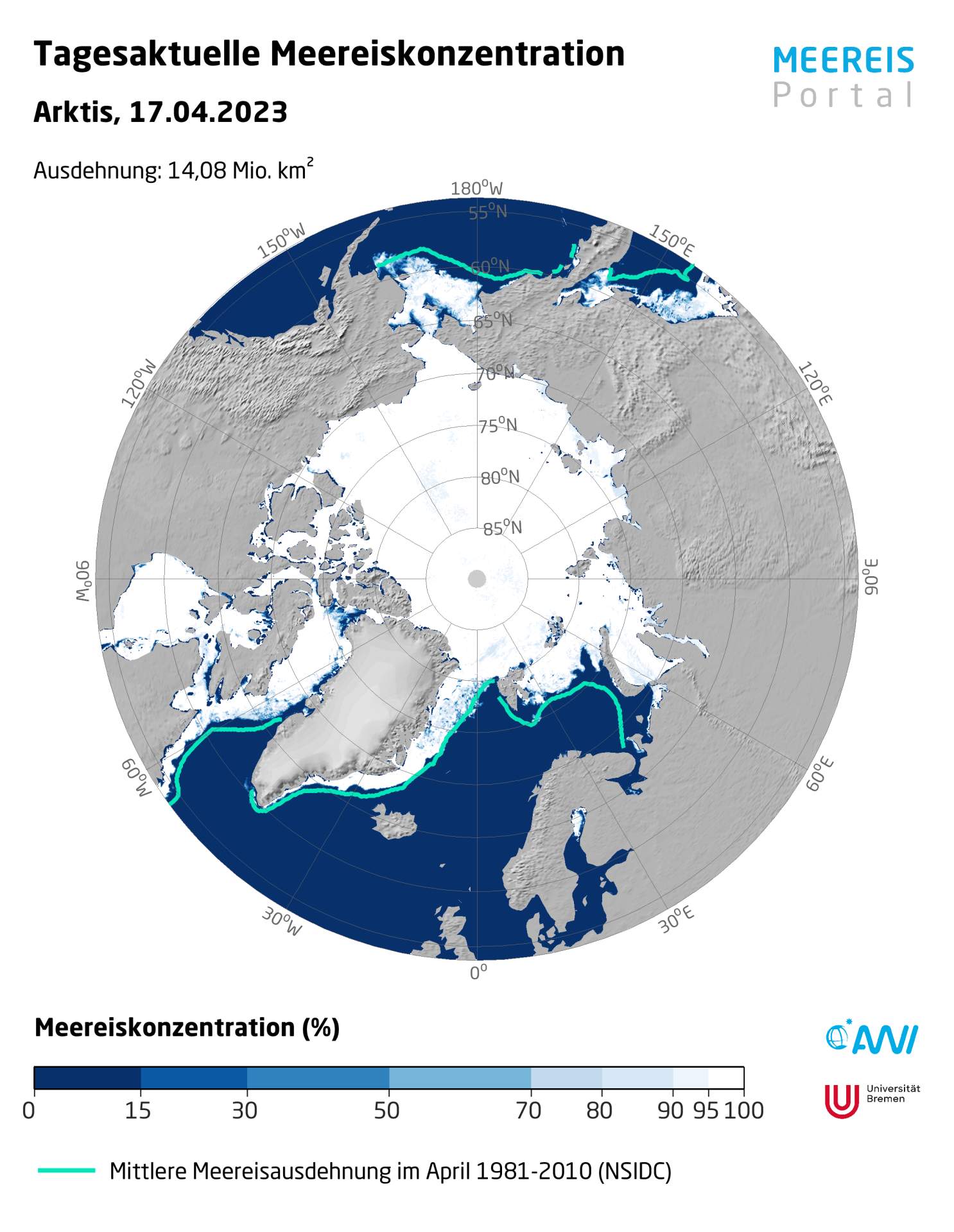
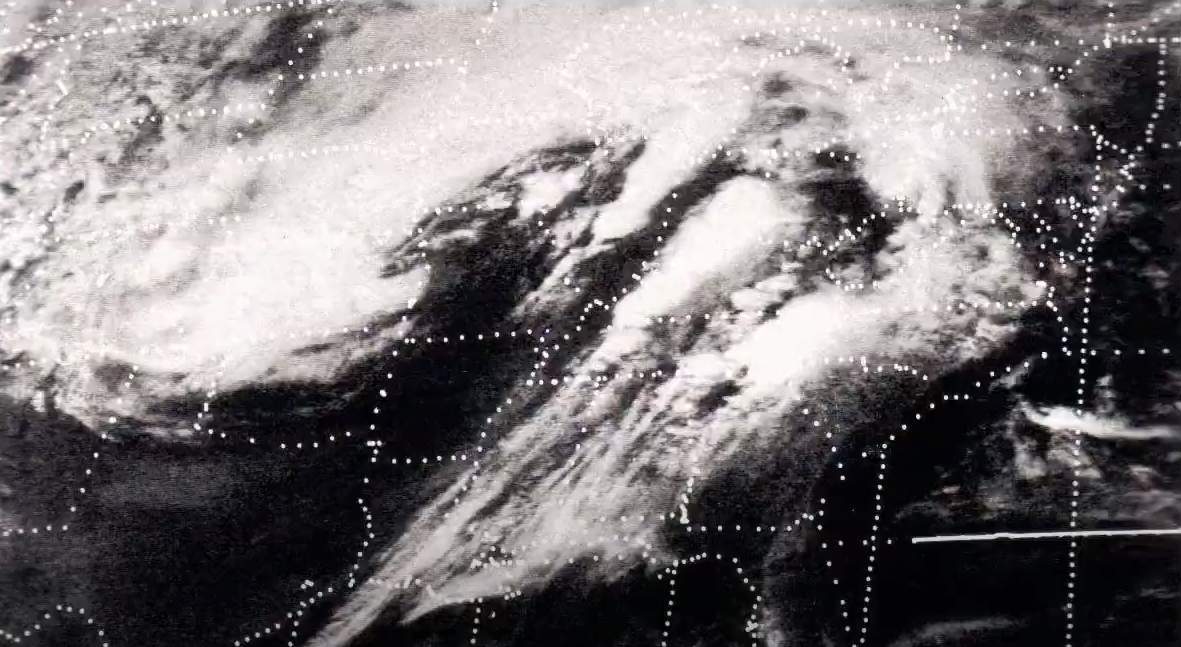
Fig. 1: Sea ice concentration on April 17, 2023; Source: meereisportal.de
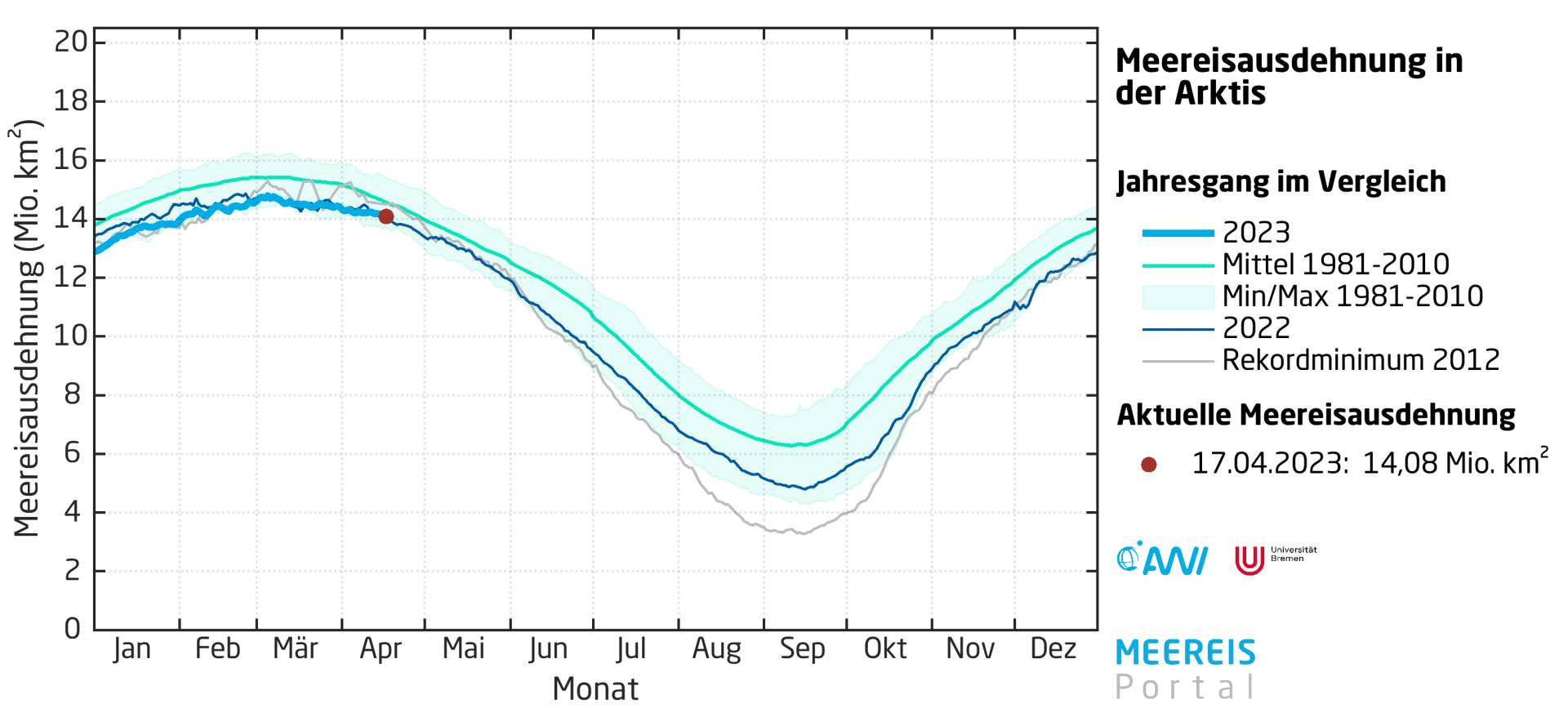
Fig. 2: Sea ice extent in the Arctic; Source: meereisportal.de
Classification of the numbers
As of April 17, 2023, the extent of sea ice is 14.08 million square kilometers (ranked 11th), which is at the lower end of what has been recorded since satellite observations began. The area covered by ice is slightly larger than the same period last year, but significantly smaller than that of 2012 at this time. At that time, the absolute record minimum was recorded later in September. Whether we get into this range in the coming months remains to be seen. However, the trend is clear! Both the maximum and minimum cover are declining – and the minima more than the maxima. Satellite data also show that the ice tends to become thinner and thus breaks up earlier.
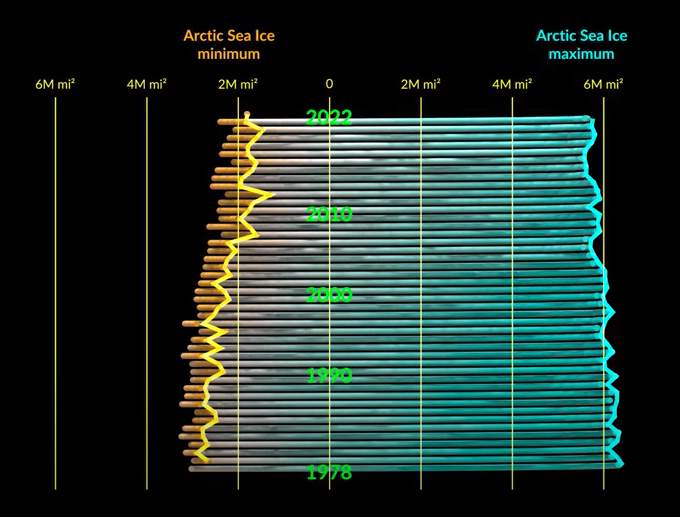
Fig. 3: Change in minimum and maximum ice cover in the Arctic since 1978.; Source: NASA
disclaimer
The content of this article has been at least partially computer translated from another language. Therefore, grammatical errors or inaccuracies are possible. Please note that the original language version of the article should be considered authoritative.